When choosing between Laravel and Node.js for web development, the right decision depends on your project requirements, development team’s skillset, and future scalability needs. Below is a comprehensive comparison to help you decide:
Though mobile apps now rule the world, web apps and websites are still vital. In case of heavy data handling, web apps are the ideal option. And with time, new frameworks and languages have been introduced to help develop these remarkable web solutions.
In this regard, Laravel and Node.js are the two most efficient and influential web development technologies. Their performance and amazing problem-solving features have significantly transformed the development industry.
What Is Laravel?

Laravel is a free, open-source PHP web application framework designed to make web development easier and faster through built-in tools and elegant syntax. It follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern and is widely used for building robust, secure, and scalable web applications. Laravel development follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which helps organize code by separating the application’s logic, user interface, and data. This structure enhances code maintainability and scalability. Laravel also maintains a clean and well-organized project directory structure, making development more efficient. Additionally, it incorporates robust security measures and supports a wide range of packages and tools—such as Voyager (admin panel), Laravel Breeze (authentication scaffolding), and Laravel Debugbar (debugging and profiling)—to accelerate and simplify the development process.
What Is Node.js?

Node.js is a runtime environment that allows you to run JavaScript code outside of a web browser, primarily used for building server-side applications. It is built on Google’s V8 JavaScript engine—the same engine that powers Chrome—and is known for its speed, scalability, and efficiency. Node.js is a single-threaded, open-source, and cross-platform runtime environment that allows developers to execute JavaScript code outside the browser, primarily for server-side development. It’s widely used to build scalable, high-performance networking and web applications.
Powered by Google’s V8 JavaScript engine, Node.js uses a non-blocking, event-driven I/O architecture, which makes it lightweight and efficient—ideal for handling real-time applications and high-concurrency workloads.
Node.js is especially valuable for developers looking to manage both the frontend and backend of an application. By learning Node.js, developers can become full-stack developers, capable of building complete applications using JavaScript across the entire stack.
. Laravel follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture
1. Model
- Represents the data and business logic.
- Interacts with the database using Laravel’s Eloquent ORM.
- Example: A User model handles user-related data and queries.
2. View
- The frontend or the user interface of the application.
- Uses Laravel’s Blade templating engine to display dynamic content.
- Example: A profile.blade.php file that shows user details.
3. Controller
- Handles user requests, processes them, and returns a response.
- Acts as a bridge between Model and View.
. Node.js the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture
Node.js can follow the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, but it doesn’t enforce it by default like Laravel does. Instead, developers manually implement MVC using frameworks and folder structure conventions.
🔧 Using MVC in Node.js
To apply MVC in Node.js, developers usually use frameworks like:
- Express.js – Lightweight and flexible framework for building web apps and APIs.
- NestJS – A more opinionated, Angular-inspired framework that enforces MVC and modular architecture.
Top Features of Laravel
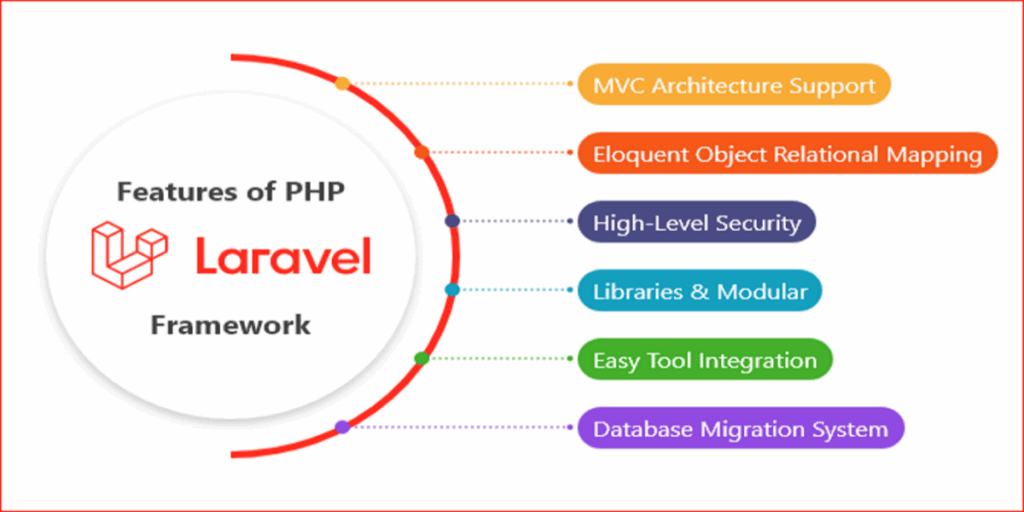
- MVC Architecture
- Blade Templating Engine
- Authentication & Authorization
- Database Migrations & Seeders
- Robust Ecosystem
- Task Scheduling
- Routing System
Top Features of Node.js
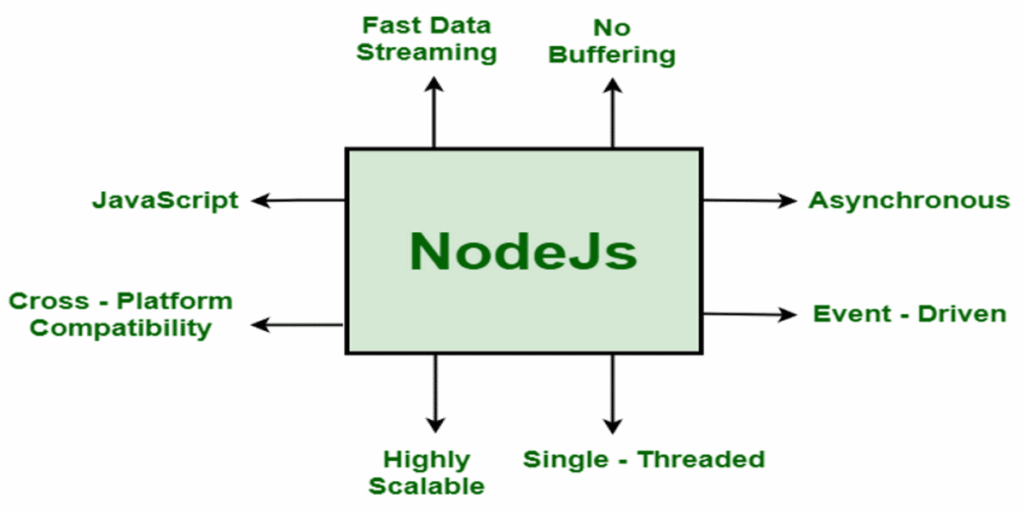
- Event-Driven, Non-Blocking I/O
- Single Language (JavaScript)
- NPM (Node Package Manager)
- Lightweight and Fast
- Microservices and APIs
- Asynchronous Programming
- Flexible Framework Choices
Laravel vs Node.js: A Detailed Comparison

1. Core Technology
| Criteria | Laravel | Node.js |
| Language | PHP | JavaScript (runtime environment) |
| Architecture | MVC (Model-View-Controller) | Event-driven, non-blocking I/O |
| Execution Model | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
2. Performance & Speed
- Laravel: Slower due to PHP’s synchronous nature. Best for apps with standard request/response cycles.
- Node.js: High performance with non-blocking I/O. Ideal for I/O-heavy and real-time applications.
3. Scalability
- Laravel: Scales well for moderate to large applications using queues, caching, and load balancers.
- Node.js: Exceptionally scalable thanks to its asynchronous model and microservices support.
4. Ease of Use & Learning Curve
- Laravel: Easier for developers with PHP background. Offers structured project layout with built-in features.
- Node.js: Requires understanding of asynchronous programming and event loops. Offers more flexibility but can be overwhelming for beginners.
5. Development Speed
- Laravel: Fast development with built-in tools like Blade, Eloquent, Artisan CLI, etc.
- Node.js: Requires assembling tools/libraries (like Express.js), which may take more setup time.
6. Community & Ecosystem
- Laravel: Large PHP community, strong ecosystem with official tools (Nova, Horizon, Forge).
- Node.js: Huge JavaScript community with millions of npm packages and widespread adoption.
7. Real-Time Capabilities
- Laravel: Possible using Laravel Echo + WebSockets or Pusher, but not native.
- Node.js: Built-in support for real-time apps (e.g., chat apps) using tools like Socket.io.
8. Security
- Laravel: Strong security features out of the box (CSRF, XSS, SQL injection prevention).
- Node.js: Security depends on chosen libraries; must be configured manually.
9. Database Handling
- Laravel: Eloquent ORM provides an elegant, easy-to-use interface for DB operations.
- Node.js: Uses ORMs like Sequelize, Mongoose (MongoDB), or Prisma (SQL). Offers flexibility but requires more setup.
10. Hosting & Deployment
- Laravel: Easily hosted on shared hosting, VPS, or platforms like Laravel Forge.
- Node.js: Typically requires VPS, containers, or cloud environments (e.g., Heroku, AWS, Vercel).
Conclusion
The best choice between Laravel and Node.js for your business website depends on your business goals, technical needs, and team expertise.
- Choose Laravel if you want:
- Rapid development with powerful built-in tools
- A structured framework with less configuration
- Backend apps like CMS, admin panels, or business apps
- Choose Node.js if you want:
- High performance and scalability
- Real-time features like chat or live feeds
- Full JavaScript stack for frontend and backend
For a traditional business website with fast development and rich backend tools, Laravel is often the better and more efficient choice.
For a highly interactive, scalable, or real-time application, Node.js offers more performance and flexibility.

